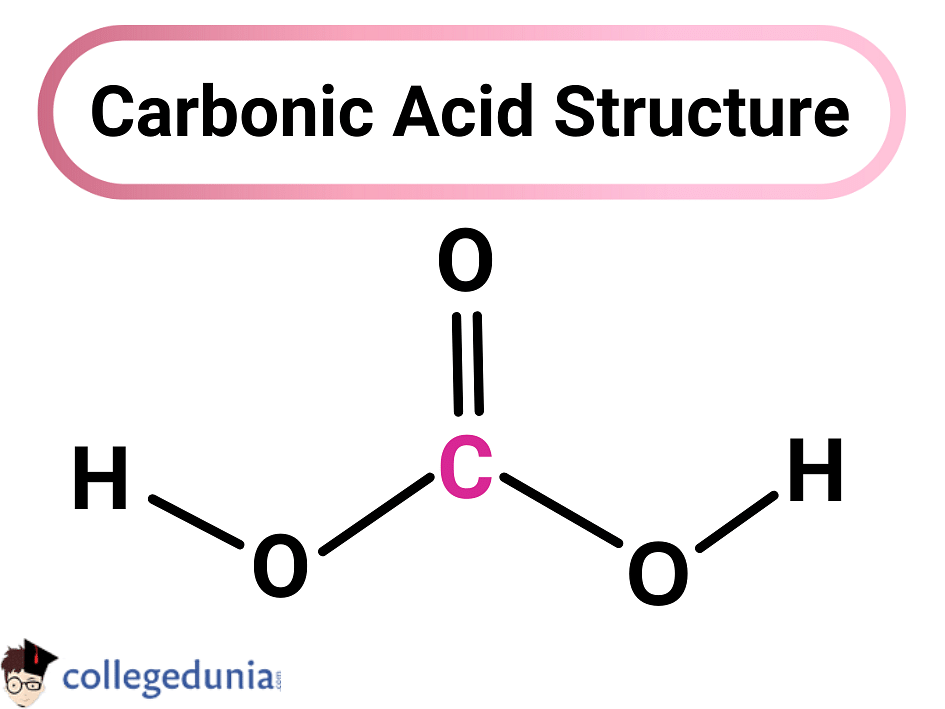
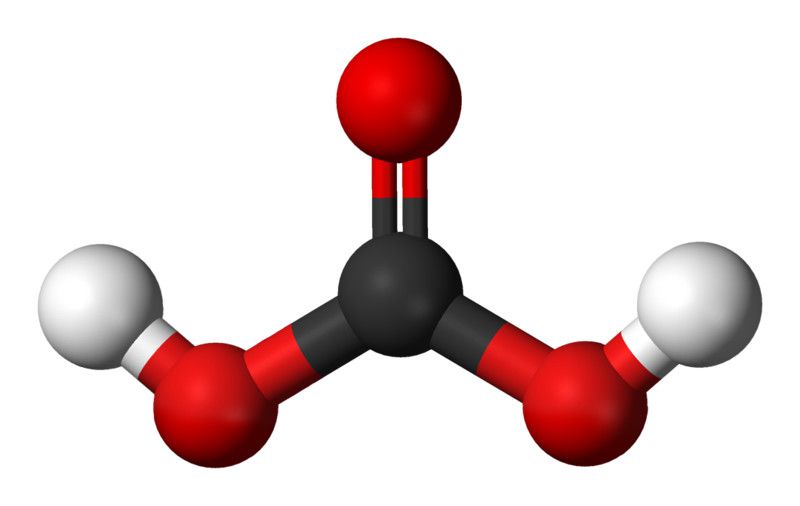
Bicarbonate-Carbonic Acid Buffer. The bicarbonate-carbonic acid buffer works in a fashion similar to phosphate buffers. The bicarbonate is regulated in the blood by sodium, as are the phosphate ions. When sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO 3), comes into contact with a strong acid, such as HCl, carbonic acid (H 2 CO 3), which is a weak acid, and NaCl.. The carbonic acid formula is H 2 C O 3, and the H 2 C O 3 compound name is carbonic acid. This means that carbonic acid is a compound, a substance made up of two or more different kinds of atoms.
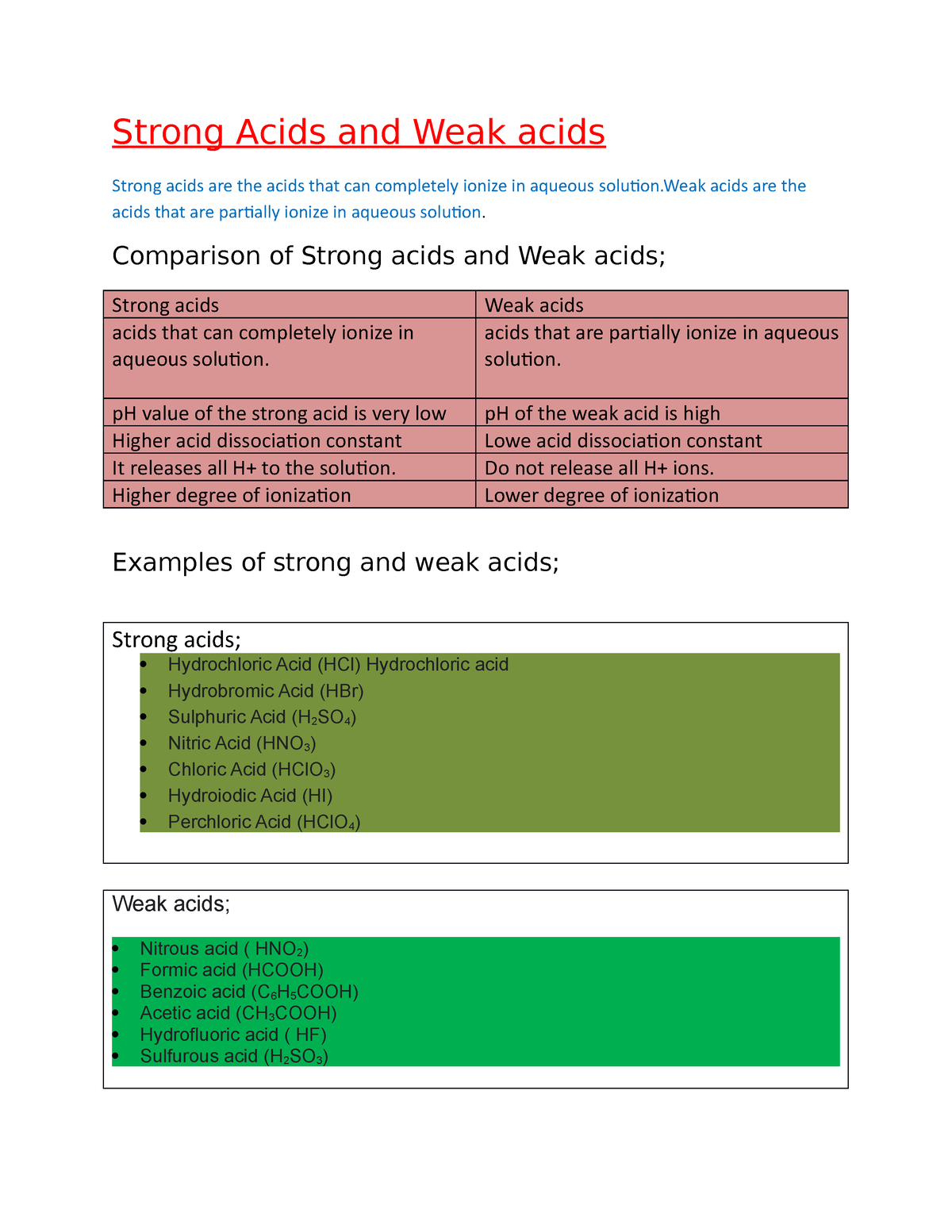
Strong Acids and Weak acids Strong Acids and Weak acids Strong acids are the acids that can

Carbonic Acid Chemical Structure Vector Illustration Stock Vector (Royalty Free) 2143333649

Concentrated Acid vs. Strong Acid (Diagram and Explanations) YouTube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/carbonic-acid-molecule-147216571-5750458f3df78c9b46a1d04d.jpg)
10 Common Acids and Chemical Structures
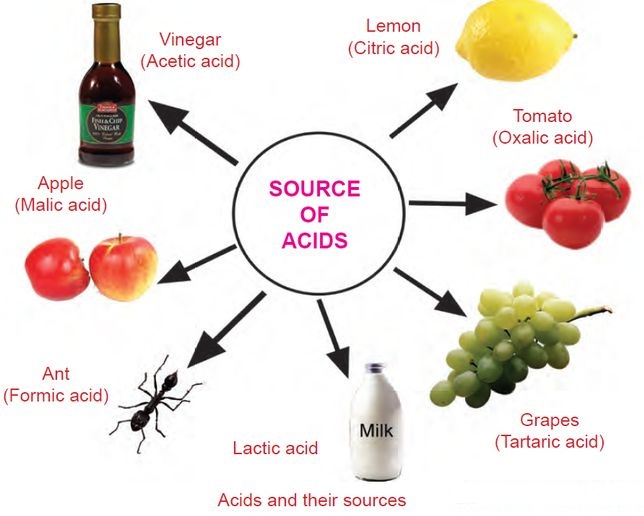
Classification of Acids according to its strength (degree of ionization), Its source & Basicity

How to Remember the Strong Acids and Bases in 2 Minutes Easily YouTube

PPT Common Strong acids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID4763569
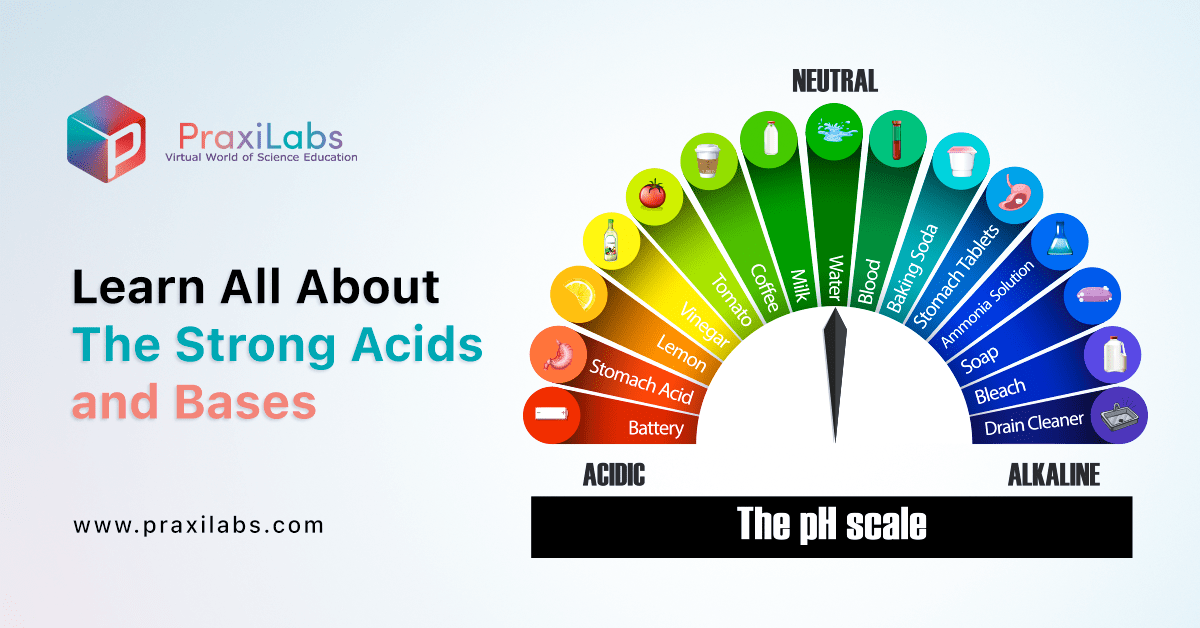
Learn All About The Strong Acids and Bases PraxiLabs
Carbonic Acid H2CO3, Structure, Properties & Uses

Strong Acid and Weak Acid
Examples of Weak Acids 5+ Examples Teachoo Teachoo Questions

Carbonic acid molecule Stock Image F018/2962 Science Photo Library

Carbonic acid (H2CO3) molecule Structural chemical formula and molecule model. Sheet of paper in
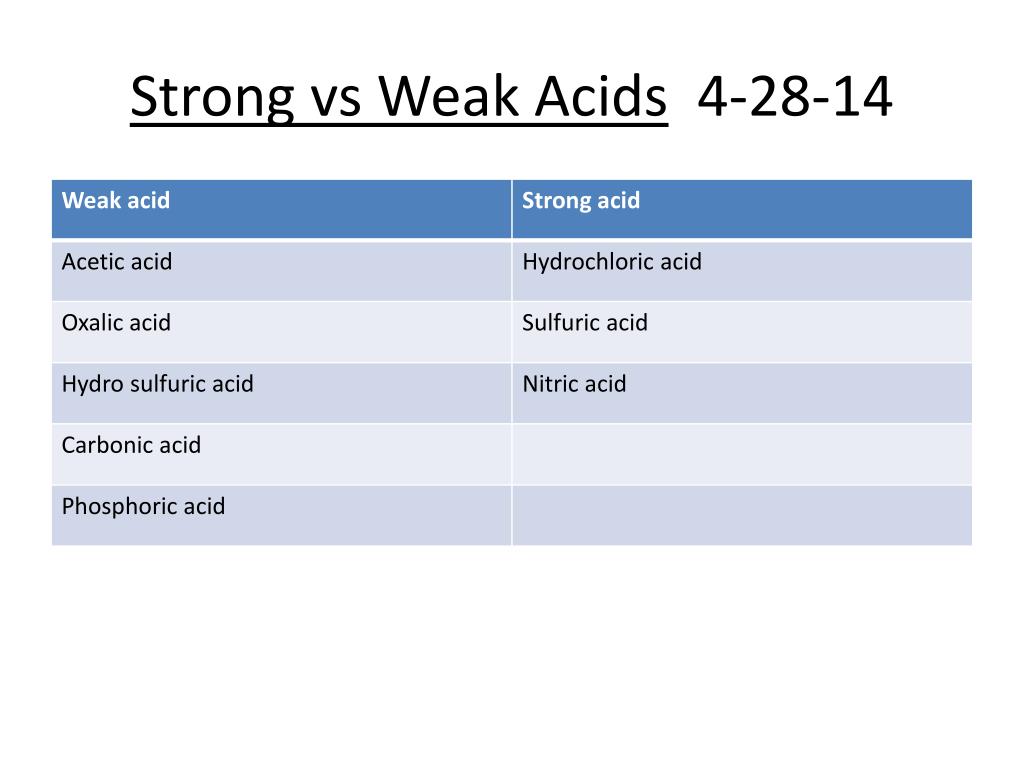
PPT Strong vs Weak Acids 42814 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2303520

PPT Strong acids vs Weak acids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2362533
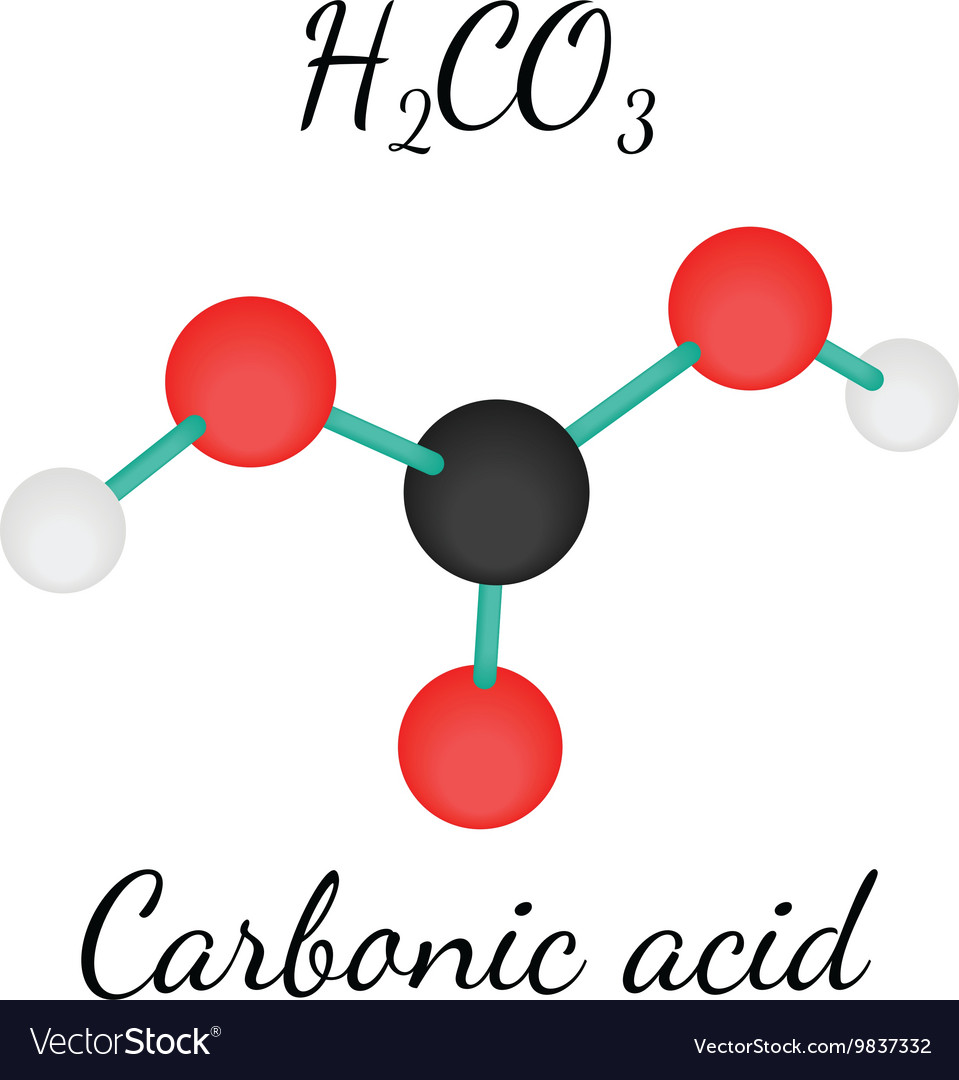
H2CO3 Carbonic acid molecule Royalty Free Vector Image
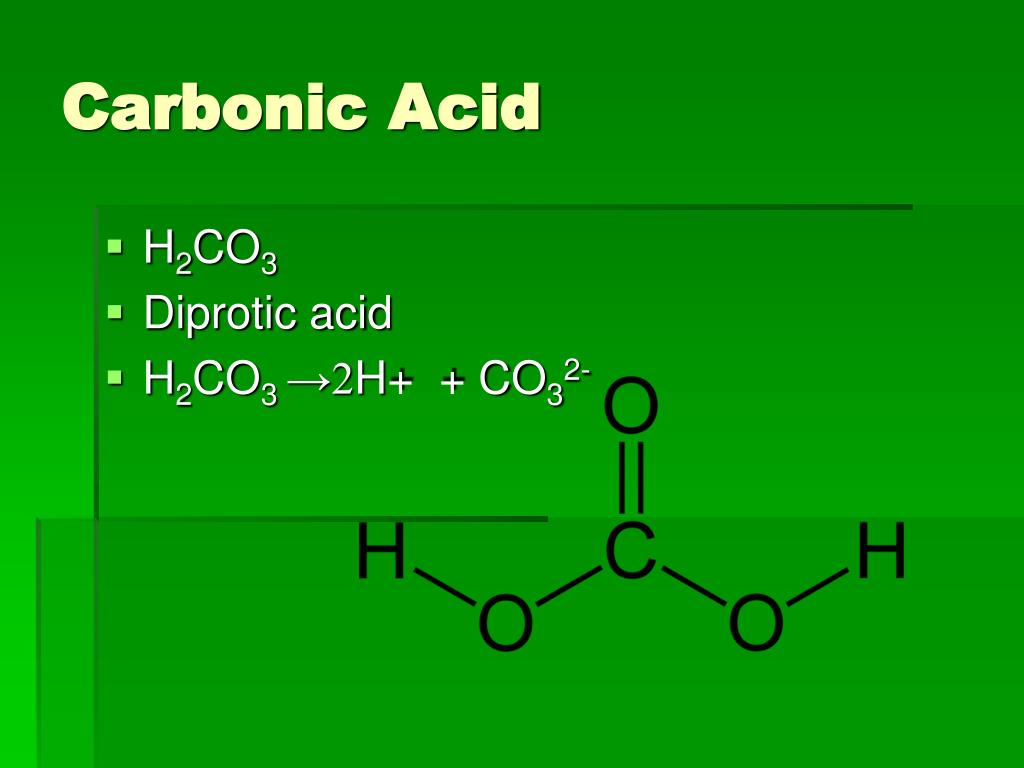
PPT Acid Base Theories 19.1 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6155947

Carbonic acid Meaning YouTube
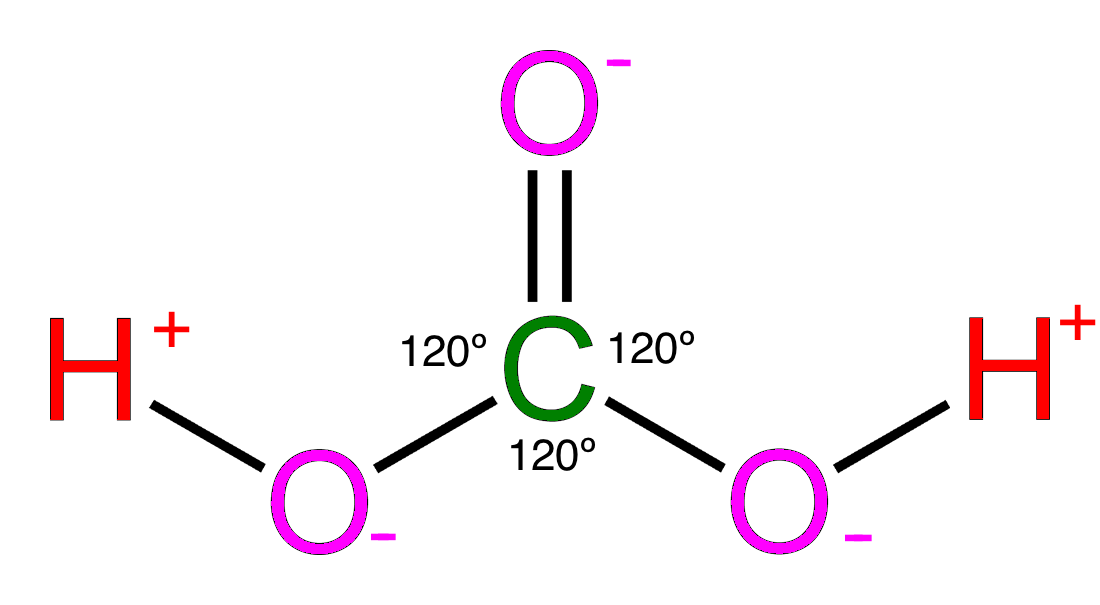
Drawing Carbonic Acid
No, carbonic acid is not a strong acid. H2CO3 is a weak acid that dissociates into a proton (H+ cation) and a bicarbonate ion (HCO3- anion). This compound only partly dissociates in aqueous solutions. Furthermore, the conjugate base of carbonic acid, which is the bicarbonate ion, is a relatively good base. These are the reasons why carbonic.. Diprotic Acids. The acid equilibrium problems discussed so far have focused on a family of compounds known as monoprotic acids.Each of these acids has a single H + ion, or proton, it can donate when it acts as a Brnsted acid. Hydrochloric acid (HCl), acetic acid (CH 3 CO 2 H or HOAc), nitric acid (HNO 3), and benzoic acid (C 6 H 5 CO 2 H) are all monoprotic acids.




